We participate, they profit
The International Fund for Agricultural Development published Good Practices in Participatory Mapping [PDF] last summer. In it they mention Sherry Arnstein’s A Ladder of Citizen Participation (JAIP, Vol. 35, No. 4, July 1969, pp. 216-224).
There is a critical difference between going through the empty ritual of participation and having the real power needed to affect the outcome of the process. This difference is brilliantly capsulized in a poster painted last spring [1968] by the French students to explain the student-worker rebellion. The poster highlights the fundamental point that participation without redistribution of power is an empty and frustrating process for the powerless. It allows the powerholders to claim that all sides were considered, but makes it possible for only some of those sides to benefit. It maintains the status quo.
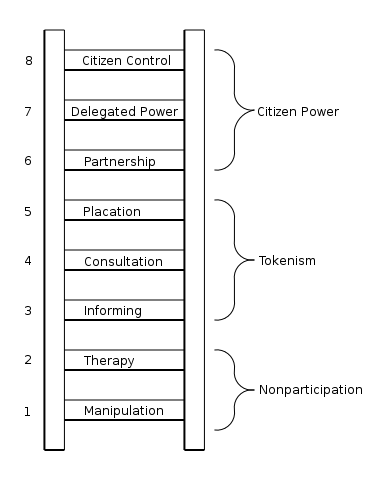
Arnstein introduces a ladder typology whose subject matter is all too familiar:
The bottom rungs of the ladder are (1) Manipulation and (2) Therapy. These two rungs describe levels of “non-participation” that have been contrived by some to substitute for genuine participation. Their real objective is not to enable people to participate in planning or conducting programs, but to enable powerholders to “educate” or “cure” the participants. Rungs 3 and 4 progress to levels of “tokenism” that allow the have-nots to hear and to have a voice: (3) Informing and (4) Consultation. When they are proffered by powerholders as the total extent of participation, citizens may indeed hear and be heard. But under these conditions they lack the power to insure that their views will be heeded by the powerful. When participation is restricted to these levels, there is no follow-through, no “muscle,” hence no assurance of changing the status quo. Rung (5) Placation is simply a higher level tokenism because the ground rules allow have-nots to advise, but retain for the powerholders the continued right to decide.
Further up the ladder are levels of citizen power with increasing degrees of decision-making clout. Citizens can enter into a (6) Partnership that enables them to negotiate and engage in trade-offs with traditional power holders. At the topmost rungs, (7) Delegated Power and (8) Citizen Control, have-not citizens obtain the majority of decision-making seats, or full managerial power.
Obviously, the eight-rung ladder is a simplification, but it helps to illustrate the point that so many have missed - that there are significant gradations of citizen participation. Knowing these gradations makes it possible to cut through the hyperbole to understand the increasingly strident demands for participation from the have-nots as well as the gamut of confusing responses from the powerholders.
Though the typology uses examples from federal programs such as urban renewal, anti-poverty, and Model Cities, it could just as easily be illustrated in the church, currently facing demands for power from priests and laymen who seek to change its mission; colleges and universities which in some cases have become literal battlegrounds over the issue of student power; or public schools, city halls, and police departments (or big business which is likely to be next on the expanding list of targets). The underlying issues are essentially the same - “nobodies” in several arenas are trying to become “somebodies” with enough power to make the target institutions responsive to their views, aspirations, and needs.